Fire safety and occupational safety and health (OSH) are important management areas to protect the lives of workers and corporate property. As industry develops and business operations expand, the risk of fire and the incidence of occupational hazards in the workplace also increase, requiring more complete management mechanisms to reduce the likelihood of accidents. In the modern working environment, fire safety and occupational safety and health should not be independently managed areas, but should form a comprehensive safety management framework through laws and regulations, technological applications and resource integration. This article will explore the relationship between fire safety and occupational safety and health management, relevant laws and regulations, the importance of resource integration, and future development directions to strengthen the attention and implementation of a safe environment by companies and workers.
Fire safety and occupational safety and health play complementary roles in enterprise management. The goal of both is to ensure the safety of the workplace and protect the lives and property of people from the threat of disasters. Fire safety mainly focuses on how to prevent fires, reduce the incidence of fires, and how to respond quickly and evacuate people when a fire occurs to avoid major casualties and property losses. This includes the installation and maintenance of firefighting equipment, fire source management, emergency response plans and employee firefighting training. On the other hand, occupational safety and health covers a wider range of workplace risk management, such as chemical leakage, machinery and equipment safety, labor health management, work environment monitoring and disaster prevention.
The correlation between the two lies in the fact that many occupational hazards may be closely related to fire risks. For example, improper storage of flammable items in industrial sites, fires caused by short circuits in electrical wires, explosions caused by chemical reactions, etc., may all cause serious occupational hazards. Therefore, in enterprise safety management, fire safety and occupational safety and health should be regarded as one, and the overall risk prevention capabilities should be improved through systematic management methods. Companies should formulate integrated safety policies to ensure that fire and occupational safety measures complement each other, such as incorporating fire risk analysis into workplace risk assessments and incorporating fire safety into occupational safety education and training to enhance employees’ resilience.
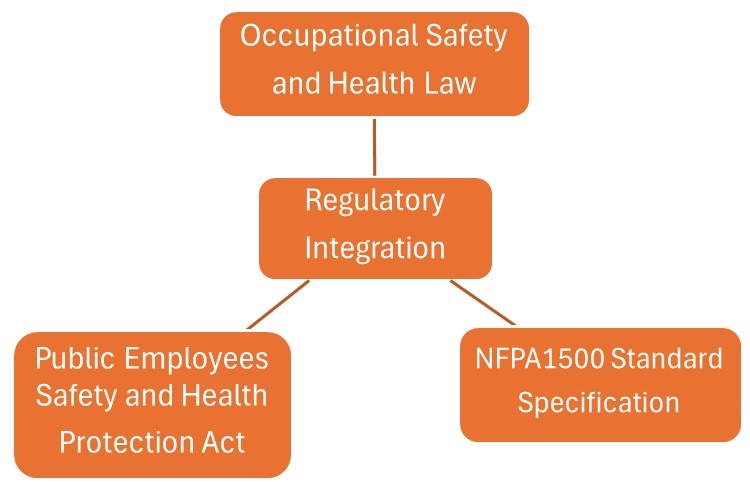
In order to ensure the safety of the working environment, all countries have formulated relevant laws and regulations to regulate the management of fire safety and occupational safety and health. Taking Taiwan as an example, the main laws and regulations involved include the Occupational Safety and Health Act, the Fire Protection Act and related sub-laws. These laws together constitute the legal basis for corporate safety management. Complying with the requirements of the laws can ensure that companies can effectively prevent accidents and enhance employees' safety awareness.
1. Occupational Safety and Health Law: This law stipulates that employers should ensure safety and hygiene in the workplace and provide appropriate equipment and measures to reduce the risk of occupational hazards. For example, places involving high-temperature operations or flammable items must be equipped with appropriate safety equipment and employees must receive relevant safety training. In addition, companies should conduct regular risk assessments to ensure that the working environment meets safety standards.
2. Fire Protection Law: This law stipulates that buildings and workplaces must meet the fire protection equipment configuration standards, including fire extinguishers, fire alarm systems, automatic sprinkler systems, etc. In addition, companies need to conduct fire inspections and drills regularly to ensure that personnel have the ability to respond to fires. The Fire Protection Law also clearly stipulates that high-risk industries (such as chemical plants and warehousing industries) must comply with stricter fire safety standards.
3. Relevant standards and specifications: In addition to the above-mentioned laws, there are many technical standards and guidelines, such as the fire safety regulations in the "Construction Technical Rules" and the "Dangerous Goods Management Measures", which set more detailed safety requirements for specific industries and working environments. Companies should ensure they comply with relevant standards and work with government regulators to ensure compliance.
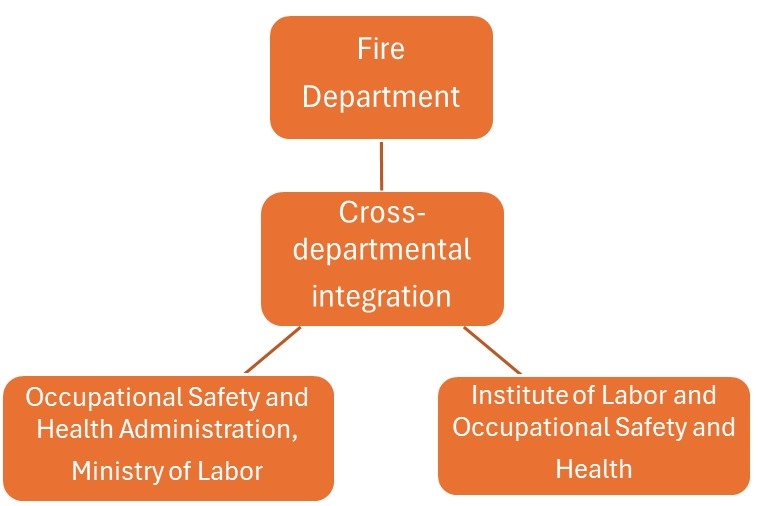
In order to improve the management efficiency of fire safety and occupational safety and health, enterprises should actively integrate internal and external resources to establish a complete safety management system.
1. Internal resource integration: Companies can establish a safety management committee to allow the fire and occupational safety and health departments to work together to formulate safety policies and standards. In addition, the introduction of digital management systems (such as IoT sensors and AI analysis tools) can monitor environmental data in real time, provide early warnings, and reduce the possibility of disasters. For example, the smart fire protection system can monitor fire alarm signals in real time and connect with the occupational safety and health system to facilitate rapid response.
2. External resource integration: Companies can cooperate with government agencies, fire departments, and occupational safety and health professional organizations to share the latest safety information and technologies. For example, participating in safety training courses organized by the government, cooperating with the fire department to conduct field drills, or working with academic institutions to develop a more complete safety management model. In addition, companies can obtain risk assessment advice from insurance institutions to further strengthen safety management.
3. Future development trends: With the advancement of science and technology, the management model of fire safety and occupational safety and health will become more intelligent and automated. For example, through artificial intelligence (AI) and big data analysis, potential risks can be predicted and preventive measures can be taken in advance; augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies can be used to improve the effectiveness of safety training; and even blockchain technology can be used to establish unalterable safety records to improve regulatory transparency. The application of these new technologies will greatly improve the safety management efficiency of enterprises and reduce the accident rate.
Fire safety and occupational safety and health management are important links in business operations that cannot be ignored. Through compliance with regulations, resource integration and technological application, enterprises can effectively reduce risks and ensure a safe and stable working environment. Modern enterprises should actively integrate the management mechanisms of fire protection and occupational safety and health, and use technology to enhance monitoring and response capabilities to cope with possible safety challenges in the future. As safety management trends towards digitalization and intelligence, if companies can make good use of these technologies and resources, they can not only reduce occupational hazards and property losses, but also improve overall operational efficiency and achieve the goal of sustainable development.
If you have any needs related to safety and health management, please feel free to contact us. Our professional team of technicians will be happy to serve you.
